Chronological List of Movies Shot Before 1900 (by GenSpark )
Abstract
This article provides a chronological list of movies shot before 1900, detailing the earliest examples of motion pictures and their significance in film history. The evolution of cinema began with early experiments in motion pictures, which laid the groundwork for future films. These pioneering efforts were crucial in shaping the medium that would become one of the most influential art forms of the 20th and 21st centuries.
The journey of motion pictures began with Eadweard Muybridge’s experiments in the late 19th century. His work, often funded by generous benefactors, reshaped the possibilities of visual content. Muybridge’s most notable experiment,
‘The Horse in Motion’ (1878),
captured a series of photographs of a galloping horse, which when viewed in sequence, created the illusion of motion. This experiment is considered one of the earliest examples of motion pictures.
In 1888, Louis Le Prince filmed
‘Roundhay Garden Scene’ in Leeds, England,
which is believed to be the first motion picture ever recorded. This short film, lasting only a few seconds, depicted four people walking in a garden. Despite its brevity, ‘Roundhay Garden Scene’ marked a significant milestone in the history of cinema, demonstrating the potential of motion pictures to capture real-life events.
The 1890s saw rapid advancements in film technology and the production of several key films. One of the most notable films from this period is
‘The Execution of Mary, Queen of Scots’ (1895),
which is recognized for its use of special effects. Directed by Alfred Clark, this short film depicted the beheading of Mary, Queen of Scots, using a clever editing trick to create the illusion of a decapitation.
Another significant film from 1895 is
‘L’Arroseur Arrosé,’
directed by the Lumière brothers. This film is considered the first comedy and depicts a simple, humorous scenario of a gardener being sprayed with water. The Lumière brothers were instrumental in the development of early cinema, and their work laid the foundation for narrative filmmaking.
The late 1890s continued to see important developments in film. In 1896, Georges Méliès directed
‘The House of the Devil,’
which is often regarded as the first horror film. Méliès, a magician turned filmmaker, used his background in stage magic to create innovative special effects, making his films visually captivating and entertaining.
By 1899, the film industry had begun to explore more complex narratives and technical aspects. Films like
‘Cinderella’
and
‘The Devil in a Convent’
showcased the evolving storytelling techniques and the increasing sophistication of special effects. These films highlighted the potential of cinema as a medium for both entertainment and artistic expression.
🎥 Early Experiments
The journey towards the creation of motion pictures began with early photographic techniques. In 1825, French inventor Nicéphore Niépce captured the oldest surviving ‘fixed’ photograph,
‘View from the Window at Le Gras,’
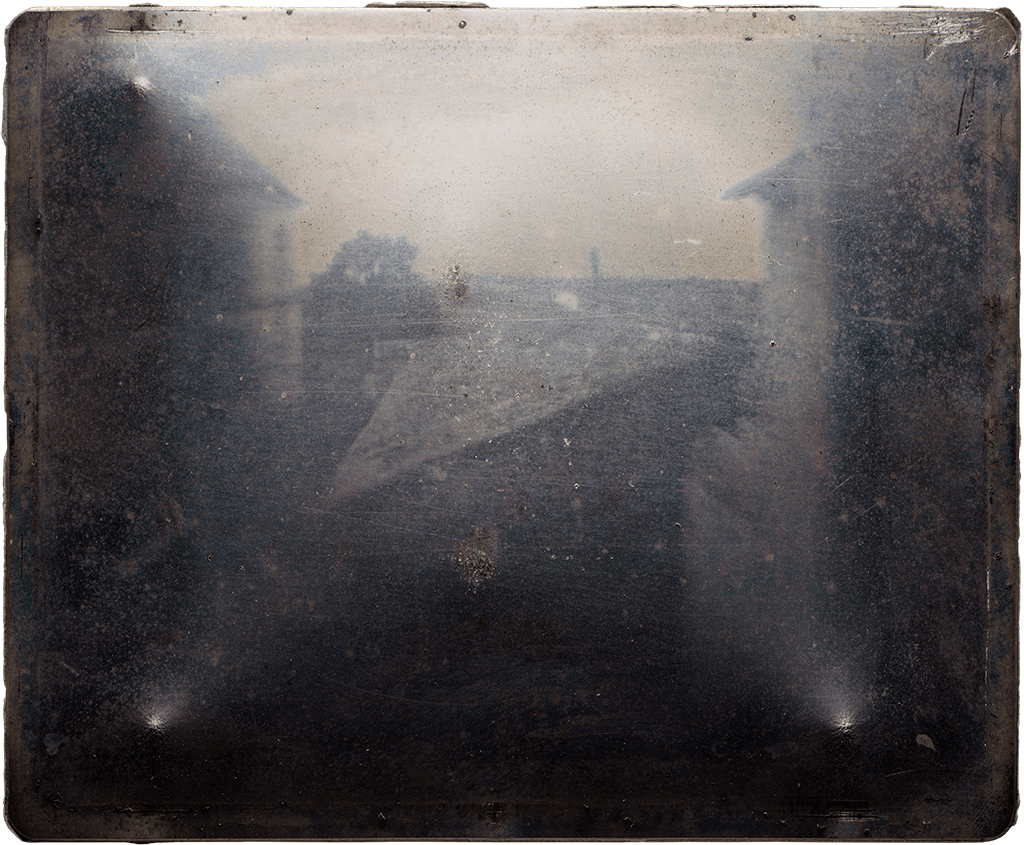
by channeling light through a camera obscura into a pewter block coated with bitumen. This groundbreaking work set the stage for fifty years of photographic experiments, leading to significant advancements by pioneers such as Louis Daguerre and William Henry Fox Talbot.
One of the earliest recognized examples of motion pictures is the work of French inventor Louis Le Prince. His 1888 film, ‘Roundhay Garden Scene,’ is considered the oldest surviving movie in the world. This short silent film, created in Leeds, England, marked a significant milestone in the history of cinema, showcasing the potential of capturing moving images.
Eadweard Muybridge’s experiments in the late 19th century were pivotal in the development of motion pictures. In 1878, using a battery of 12 cameras, Muybridge recorded ‘The Horse in Motion,’ capturing successive phases of movements. This technique, known as chronophotography, allowed his patron Leland Stanford to study the positions of his racehorses’ legs during different gaits, laying the groundwork for future motion picture technology.
The late 1880s saw various inventors around the world racing to develop innovative ways to capture and exhibit moving images. Among these early cinema innovators were Thomas Edison, Georges Méliès, William K.L. Dickson, and Auguste and Louis Lumière. Their contributions were crucial in the evolution of motion picture technology, leading to the creation of films that could be considered the first true movies.
The first public cinema screening took place on December 28, 1895, in Paris, thanks to the Lumière brothers. This event marked a significant milestone in the history of cinema, as it showcased the potential of motion pictures to a wider audience. The Lumière brothers’ work, along with that of other pioneers, laid the foundation for the future of filmmaking, transforming it into a popular form of entertainment.

headsup.scoutlife.org
🎬 1880s Milestones
The 1880s marked a significant period in the history of motion pictures, with several key films representing the earliest surviving examples of this burgeoning art form. One of the most notable milestones was achieved by French inventor Louis Le Prince, who is credited with creating the earliest surviving film, ‘Roundhay Garden Scene,’ in 1888. This groundbreaking film was shot in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England, and featured a brief sequence of people walking in a garden, captured at an impressive 20 frames per second.
In addition to ‘Roundhay Garden Scene,’ Le Prince also created other short films during the same period, including
‘Accordion Player’
and
‘Traffic Crossing Leeds Bridge.’
These films, like ‘Roundhay Garden Scene,’ were pioneering works that demonstrated the potential of motion picture technology and laid the groundwork for future developments in the field.
Another significant contribution to the early history of motion pictures came from American inventors George Eastman and Hannibal Goodwin, who in 1885 invented a sensitized celluloid base roll photographic film. This innovation replaced the glass plates that were previously in use and made it possible to capture motion pictures more efficiently and effectively.
The 1880s also saw the creation of
‘L’homme Machine,’
directed by French scientist Étienne-Jules Marey. This film is recognized as the oldest black and white animated film, showcasing Marey’s interest in studying human and animal movement through motion pictures.
In 1886, Alice Guy Blache created
‘La Fee aux Chou,’
also known as ‘The Fairy of the Cabbages,’ in France. This film stands out as one of the earliest examples of narrative filmmaking, highlighting the creative possibilities of the medium beyond mere documentation of movement.
Louis Le Prince continued to innovate with his 16-lens device, for which he was granted an American dual-patent in 1886. This device combined a motion picture camera with a projector, further advancing the technology needed to capture and display moving images.
In 1887, Le Prince directed
‘Man Walking Around a Corner,’
which is considered the oldest known film. Although it was essentially a series of photographs taken with Le Prince’s 16-lens camera, it represented a crucial step towards the development of continuous motion pictures.
📽️ 1890-1894
The early 1890s marked a significant period in the development of film technology, with several notable films showcasing the rapid advancements in the medium. One of the earliest examples from this period is
‘Dickson Greeting’ (1891),
a short film directed by William K.L. Dickson. This film is particularly significant as it was one of the first films shown publicly on the Kinetoscope, a pioneering motion picture exhibition device developed by Thomas Edison.
In 1892, Émile Reynaud released
‘Le Clown et ses chiens,’
‘Pauvre Pierrot,’
and ‘Un bon bock,’
which are considered the first projected animated films. These films were shown using Reynaud’s Théâtre Optique, an innovative system that allowed for the projection of animated sequences, marking a significant milestone in the history of animation. 9
The year 1893 saw the creation of
‘Blacksmith Scene,’
directed by William K.L. Dickson. This film is notable for being the first film shown publicly on the Kinetoscope. Additionally, 1893 was the year Thomas Edison established ‘America’s First Film Studio,’ known as the Black Maria, which played a crucial role in the development of early American cinema.
In 1894, the film industry continued to evolve with the release of several significant films. Among them were ‘Dickson Greeting,’
‘Men Boxing,’ 1891
and ‘Newark Athlete,’
all directed by William K.L. Dickson. These films were instrumental in demonstrating the potential of motion pictures as a form of entertainment and documentation.
🎞️ 1895
The year 1895 stands as a cornerstone in the history of cinema, marking the first commercial public screening of films. On December 28, 1895, the Lumière brothers, Auguste and Louis, showcased ten short films at the Salon Indien du Grand Café in Paris. This event is traditionally celebrated as the birth of cinema, as it was the first time films were shown to a paying audience.
Among the significant films from 1895 is
‘Workers Leaving the Lumière Factory,’
directed by the Lumière brothers. This short film, depicting workers leaving the Lumière factory, is often cited as one of the first motion pictures ever made. It exemplifies the early documentary style that would become a staple in the film industry.
Another notable film from 1895 is ‘The Execution of Mary, Queen of Scots,’ directed by Alfred Clark. This film is significant for its use of special effects, specifically the stop trick, which created the illusion of a beheading. This innovative technique demonstrated the potential of film to create visual illusions and tell more complex stories.
‘Annabelle Serpentine Dance,’ also from 1895,
features dancer Annabelle Moore performing a serpentine dance. This film is notable for its use of hand-tinted color, which added a new dimension to the visual experience. The film’s vibrant colors and graceful movements captivated audiences and showcased the artistic possibilities of the medium.
The Lumière brothers also produced
‘Tables Turned on the Gardener’ in 1895,
a comedic short film that is often considered one of the first narrative films. The film tells a simple story of a gardener who gets sprayed with water by a mischievous boy, only to turn the tables on the boy. This early example of slapstick comedy highlighted the potential for storytelling in film.
In addition to these films, 1895 saw the creation of
‘Boat Leaving the Port,’
another Lumière brothers’ production. This film captures a boat departing from a port, showcasing the everyday life and activities of the time. It is an early example of the documentary genre, capturing real-life events and people.
The year also witnessed the production of
‘The Boxing Kangaroo,’
a film that featured a kangaroo engaging in a boxing match with a human. This film is significant for its novelty and entertainment value, demonstrating the diverse range of subjects that early filmmakers explored.
1895 was indeed a pivotal year in the history of cinema, with numerous significant films that showcased the rapid development of film technology and storytelling techniques. These early films laid the foundation for the future of cinema, demonstrating the medium’s potential for both artistic expression and entertainment.
📹 1896-1899
The period from 1896 to 1899 was a transformative era in the history of cinema, marked by significant advancements in both narrative and technical aspects of filmmaking. This era saw the production of numerous pioneering films that laid the groundwork for modern cinema.
In 1896, the Lumière brothers released
‘The Arrival of a Train at La Ciotat,’
a film that famously startled audiences with its realistic depiction of a train approaching the camera. This film is often cited as one of the earliest examples of the power of cinema to evoke strong emotional reactions from viewers.
Another notable film from 1896 is ‘The Cabbage Fairy,’ directed by Alice Guy-Blaché. This film is significant as it is one of the earliest examples of narrative filmmaking, featuring a whimsical story about a fairy who conjures babies from cabbages.
Georges Méliès, a key figure in early cinema, released several important films during this period. In 1896, he directed
‘The Haunted Castle,’
which is considered one of the first horror films. Méliès’ use of special effects and innovative storytelling techniques had a profound impact on the development of narrative cinema.
The year 1897 saw the release of
‘The Bewitched Inn,’
another film by Georges Méliès. This film showcased Méliès’ talent for creating magical and fantastical scenes, further establishing his reputation as a pioneer of special effects in cinema.
In 1898, the film
‘The Four Troublesome Heads,’
directed by Georges Méliès, demonstrated the use of multiple exposures to create the illusion of a man removing and replacing his own heads. This film is an early example of the creative possibilities of in-camera effects.
The year 1899 was particularly notable for the release of ‘Cinderella‘ by Georges Méliès. This film is one of the earliest adaptations of the classic fairy tale and is significant for its use of elaborate sets, costumes, and special effects to tell a coherent and engaging story.
Another important film from 1899 is
‘The Dreyfus Affair,’
also directed by Georges Méliès. This film is a multi-part series that dramatizes the infamous political scandal in France. It is one of the earliest examples of a film series and showcases Méliès’ ability to tackle complex and controversial subjects.

Leave a comment